

These scholars tend to focus on what the entrepreneur does and what traits an entrepreneur has (see for example the text under the headings Elements below). Some view entrepreneurship as allocated to the entrepreneur. It has been studied within disciplines such as management, economics, sociology, and economic history. Īs an academic field, entrepreneurship accommodates different schools of thought. After the end of supply-side economics, entrepreneurship was supposed to boost the economy. In the 21st century the governments of nation states have tried to promote entrepreneurship, as well as enterprise culture, in the hope that it would improve or stimulate economic growth, and competition.

In this sense, entrepreneurship describes activities on the part of both established firms and new businesses. In the field of economics, the term entrepreneur is used for an entity which has the ability to translate inventions or technologies into products and services. While definitions of entrepreneurship typically focus on the launching and running of businesses, due to the high risks involved in launching a start-up, a significant proportion of start-up businesses have to close due to "lack of funding, bad business decisions, government policies, an economic crisis, a lack of market demand, or a combination of all of these." More narrow definitions have described entrepreneurship as the process of designing, launching and running a new business, which is often similar to a small business, or as the "capacity and willingness to develop, organize and manage a business venture along with any of its risks to make a profit." The people who create these businesses are often referred to as "entrepreneurs". The entrepreneur is commonly seen as an innovator, a source of new ideas, goods, services, and business/or procedures. The process of setting up a business is known as "entrepreneurship".

With this definition, entrepreneurship is viewed as change, generally entailing risk beyond what is normally encountered in starting a business, which may include other values than simply economic ones.Īn entrepreneur is an individual who creates and/or invests in one or more businesses, bearing most of the risks and enjoying most of the rewards. I think I got most of them right, but if you have any tips please let me know below.Entrepreneurship is the creation or extraction of economic value. Allocative inefficiency is also wasteful because we're producing too much of a good that is not being used, while we're lacking in another. The war affected Germany's PPF by making it harder to produce goods, because they lost resources. Allocative efficiency is when the combination of goods produced is exactly what a society needs.ħ. Productive efficiency is when you can't produce more of a good without decreasing the amount that another good is produced. Diminishing marginal returns happen when you exceed the optimal limit of producing a product, thus making the marginal returns drop.Ħ. And they shouldn't make a choice in it because it's inefficient and does not use all available resources.ĥ. A society cannot make a choice above (or out) of the PPF because they don't have enough resources to do so. Everything inside the curve is inefficient and everything outside is impossible.Ĥ. Because the curve shows the most efficient ways an economy can produce the products, using all the given resources. A PPF illustrates the efficient ways an economy can produce two products, with their available resources.ģ. A comparative advantage is when a country can produce a good faster and/or cheaper than another country, giving them an advantage over that good.Ģ.
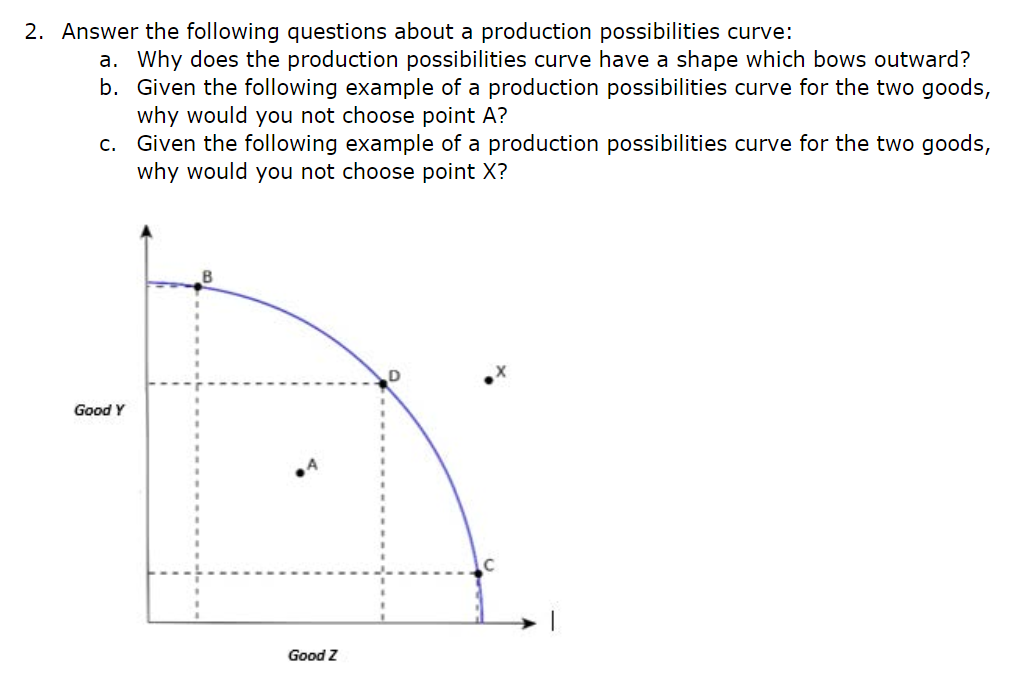
For this reason, the shape of the PPF from A to B is relatively flat, representing a relatively small drop-off in health and a relatively large gain in education.ġ. However, putting those marginal dollars into education, which is completely without resources at point A, can produce relatively large gains. Diverting some resources away from A to B causes relatively little reduction in health because the last few marginal dollars going into healthcare services are not producing much additional gain in health. Now imagine that some of these resources are diverted from healthcare to education, so that the economy is at point B instead of point A. People are having cosmetic surgery on every part of their bodies, but no high school or college education exists. For example, children are seeing a doctor every day, whether they are sick or not, but not attending school. This situation would be extreme and even ridiculous. At point A, all available resources are devoted to healthcare and no resources are left for education. To understand why the PPF is curved, start by considering point A at the top left-hand side of the PPF.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
